Archives
-

Gebhardt, Marc: Erweiterung und Vergleich von Leistungsflusszerlegungsmethoden
Vol. 104 (2025)The European transmission grid is characterized by a highly meshed grid structure and a comprehensive network of several transmission system operators. These connections mean that power flows occurring in one market region also affect other regions due to line impedances and the load situation in the system. Furthermore, additional power flow control systems such as phase-shifting transformers and high-voltage direct current lines have been installed in recent years and will be installed on a larger scale in the future. Based on the operational concepts applied, these elements will lead to additional power flows that can have a burdening or relieving effect on the assets of the system. A classification of the various partial power flows defined by ENTSO-E is extended in this work and then used to map the effects of individual generator-load pairs and the power flow-controlling equipment in the grid in a uniform and systematic way.
Due to the possible negative effects on the transmission capacities, the quality and quantity of the different flow types are determined in the work depending on the calculation method. It is necessary to compare the different algorithms, as each method is based on different mathematical descriptions of the flow types and uses different simplifications to separate the power flow. In this paper, Full Line Decomposition, Power Flow Coloring and Power Flow Decomposition are explained and compared. An important factor is the extension of the methods to recognize the influences of phase-shifting transformers and high-voltage direct current lines. Therefore, all three methods are extended so that the
extended flow categories can be calculated with each method. The advantages and disadvantages of the individual methods are then worked out and a recommendation for the application of the algorithms is made.ISBN: 978-3-948749-58-3
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2025-088
-

Rodrigues Lautert, Renata: Grid and system-oriented use of flexibility provided by energy communities
Vol. 103 (2025)In the current energy transition scenario, the power system has been incorporating actions aimed at decentralizing energy generation, digitalizing the system, decarbonizing, dereg- ulating and democratizing access to electricity. The concept of an energy community (EC) matches these aspects, promoting sustainability and increasing flexibility. The aim of this dissertation is to develop a control model for an EC that encompasses three different levels of flexibility and incentives for the use of flexibility. The simulated EC operates exclusively with renewable energy sources, uses a battery energy storage system (BESS) and integrates an electric vehicle (EV). Power dispatch was implemented using rule-based and optimization methods based on mixed-integer linear programming. The EC is inserted into the energy market, allowing transactions with the grid using a real-time tariff. Economic viability was assessed by calculating the daily operating cost. The main objective of the optimization was to minimize costs while prioritizing the use of available renewable resources. The analysis was conducted considering four days rep- resentative of the seasons. Scenarios of excess generation and low demand, along with low generation and high demand, were simulated to validate the proposed methodology. The three levels of flexibility were configured using adjustable parameters, including the initial and final state of charge of the BESS, the weighting coefficients for charging and discharging the BESS and the EV. These levels range from F1, the most flexible, to F3, the most conservative. Incentives in the form of rewards were introduced in accordance with the EC use of flexibility. In addition, an analysis of the voltage levels on the EC buses was performed, verifying compliance with the normative standards. The results demonstrated that the optimization model was more efficient in managing energy, guaranteeing that loads were met throughout the period analyzed. The EC's rev- enue increased by 30% in the worst-case scenario and exceeded three times the revenue, in the most beneficial scenario when using the optimized method. The behavior of BESS and EV was crucial both technically and economically, as the strategy of charging in times of surplus or low tariffs and discharging in times of deficit or high prices increased flexibility and reduced costs. In all scenarios, voltages remained within regulatory limits, even under extreme conditions. The proposed model has been shown to promote flexibil- ity and efficiency, ensuring safe operation in alignment with sustainability objectives.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-57-6
-

dos Santos Ortiz, Mauro: Forecasting model for the integration of battery electric vehicles into the power grid using system dynamics
Vol. 102 (2024)Growing discussions about the depletion of natural resources and the environmental risks arising from the extensive use of fossil fuels in the productive sectors are mobilizing public and private agents to rethink strategies for sustainable economic and social development. At the same time, various research projects are being conducted with a focus on generating energy from renewable sources and developing technologies and strategies for the efficient and intelligent use of energy. In the transportation sector, which is responsible for high emissions of greenhouse gases, electric vehicles ( EVs) are a promising alternative. The global market for EVs is currently booming, and the outlook is good for a decrease in acquisition costs, especially battery costs. It is also expected that the range of vehicles will increase and the charging infrastructure will improve. Moreover, the formulation of public policies and subsidies for the purchase of EVs represent major incentives for their adoption, especially by residential consumers. However, whether they buy an EV or not depends on the value judgment and subjectivity of each human being. In the literature, studies can be found, that discuss the penetration of EVs in a specific way and are restricted to a few variables. For this reason, the aim of this doctoral thesis is to develop a global model for forecasting the diffusion of battery electric vehicles ( BEV s) among residential consumers, analyzing the variables that influence their decision-making. To do this, the system dynamics ( SD ) technique is used together with the Bass model, considering quantitative and qualitative aspects of decision-making to determine the diffusion of BEVs over time. Additionally, the model encompasses the analytic hierarchy process ( AHP) and fuzzy logic to address the uncertainties and region-specific characteristics that influence BEV adoption. Case studies in Brazil and Germany demonstrate the model’s flexibility and accuracy in forecasting adoption trends and highlight the different impacts of public policies, infrastructure, market conditions, among others. In addition to the academic and scientific contributions, the developed model can support governments in formulating public policies to promote electric mobility. For companies in the energy sector, it provides important information for studies on the expansion of the electrical energy system. It also helps automotive companies align their sales strategies and expand their business models.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-53-8
-
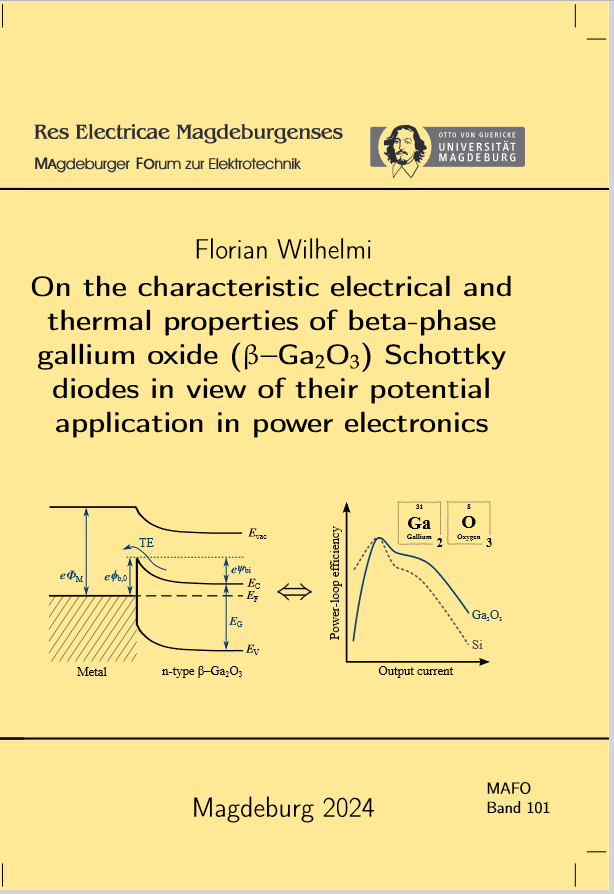
Wilhelmi, Florian: On the characteristic electrical and thermal properties of beta-phase gallium oxide (β–Ga2O3) Schottky diodes in view of their potential application in power electronics
Vol. 101 (2024)The semiconductor beta gallium oxide (β–Ga2O3) combines a 4.6–4.9 eV wide band gap with the availability of melt-grown wafers and could help meet the growing demand for high-efficiency and low-cost power electronics. However, research still mostly focuses on basic device structures, and the low thermal conductivity raises concerns about potential thermal management problems. The objective of this work is to transition from fundamental device structure research to power electronics applications by experimentally and through simulation investigating the electrical and thermal characteristics of novel β–Ga2O3 diodes from a planned production line. A change of the conduction mechanism leading to an initial decrease and then increase of the conduction losses with rising temperature is observed for multiple but not all diodes. This seems to originate from the device processing rather than the intrinsic properties of β–Ga2O3. Despite a strong variation of the material properties between diodes of the same type, a lower increase in differential on-resistance with rising temperature is observed compared to silicon carbide (SiC) diodes, and measurements of the temperature-dependent ideality factors and Schottky barrier heights indicate stable junction properties. The heat dissipation in Ga2O3 diodes can be improved by thinning the currently 600 μm thick standard devices to thicknesses of 200 μm. In contrast to SiC, however, cooling the devices from the junction side is found to be significantly more effective in reducing the junction temperature despite the smaller cooling area, if the entire anode area is covered with die-attach material. Combined with the potentially low conduction losses, it seems realistic for future Ga2O3 diodes to achieve similar junction temperatures as modern commercial SiC diodes at the same forward current. Even 600 μm thick diodes are successfully implemented in a 400 V buck converter operated at frequencies up to 350 kHz. Peak voltage slew rates exceeding 100 V/ns are achieved, but in continuous operation the diodes exhibit a higher temperature rise than their SiC counterparts. Nevertheless, the efficiencies with a state-of-the-art silicon diode of similar size can be surpassed with the Ga2O3 diodes despite the still higher on-resistance, owing to the absence of recombination losses.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-49-1
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2024-087
-

Helm, Sebastian: Optimiertes Lademanagement von E-Kfz zur Spannungsstabilisierung im Niederspannungsnetz
Vol. 100 (2024)In the context of climate-friendly energy generation and the reduction of the share of fossil fuels in the sectors of electricity, heat and transport, the integration of renewable energies continues. As a result of the long-term increase in energy prices, there is also a growing desire on the part of private individuals for energy independence as well as self-sufficiency with energy. This leads to a strong increase in single-phase and three-phase connected PV systems and battery storage systems as well as three-phase connected heat pumps, which in turn leads to new conditions due to the much higher rated power of the facilities. The transformation of the transportation sector and the push for electric mobility with 1,000,000 vehicles registered during 2021 will lead to a further increase in single-phase and three-phase loads. Low-voltage grids, in contrast to other grid levels, have the peculiarity that loads are largely connected in single-phase, as the operating equipment often has low loads. The much higher rated powers of PV systems, battery storage, heat pumps and electric vehicles have a direct impact on grid stability and are reflected by low and unbalanced grid voltages on the phases. This work deals with the balancing as well as the voltage stability of the three phases in the low-voltage grid using intelligent "Grid-to-Vehicle" (G2V) as well as "Vehicle-to- Grid" (V2G) applications of electric vehicles. Initially, the definition of unbalance and limit values as well as the calculation of unbalanced load flows is conducted. It is ana- lyzed how loads with both single-phase and three-phase grid connection generate unbalances. This is followed by the development of a G2V approach to balancing and a V2G approach to balancing and voltage stability. Based on existing measured values, given by the charging infrastructure, an optimization approach is applied to determine an optimal charging or discharging power to stabilize the grid state. Conceptually, no communication technology connection or stored network topologies in the electric vehicle are assumed. Within the framework of simulations for the defined scenarios 2020, 2025 as well as 2030, the function of the developed solution is demonstrated and the approaches without adaptation of the charging power are compared with G2V and V2G. The fundamental verification of the developed G2V approach is carried out within the framework of a hardware test. In a laboratory test, the G2V approach is implemented in an e-vehicle and the compensation of voltage unbalance is evaluated.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-48-4
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2024-086
-

Middelstädt, Felix: Electromagnetic field coupling to thin wires above the ground
Vol. 99 (2024)Transmission lines play an important role in many electronic and electrical systems. They guide signals and power between different components. However, they can also act unintentionally as an antenna that receives surrounding electromagnetic fields that might destroy sensitive components. Furthermore, the transmission line might emit electromagnetic fields that could interfere with other devices in the same environment. Hence, the analysis of the transmission line is important, especially in the context of electromagnetic compatibility analysis. There are different kinds of transmission lines, e.g. microstrip lines on printed circuit boards or thin wires above a large ground plane. The goal of this thesis is the analytic and semi-analytic analysis of the current along thin wires above a large ground plane in frequency domain. The general understanding of the wave propagation along and the field coupling to this important class of transmission lines shall be improved by this work. The considered thin wires are excited by a plane wave. They are assumed to be long compared to the wave length and must have a uniform section somewhere along the trajectory. Apart from the uniform section the trajectory of the wire can be arbitrary and lumped impedances can be present at the ports. Multiple wires above a ground plane are considered as well. For these transmission lines the so called asymptotic approach is applicable. It provides an analytic expression for the current in the uniform section of the wire and plays a key role in the analytic and semi-analytic analysis of the current. It is assumed that the current in the uniform section is a superposition of transverse electromagnetic modes and a forced response. The amplitudes of these modes depend on the scattering and reflection coefficients of the wire ports. These coefficients are in general complex, frequency dependent and consider the trajectory of the wire at the ports. They might include high frequency effects like radiation at discontinuities. This is a notable difference to the classical transmission line theory. Hence, the asymptotic approach is applicable to much higher frequencies than the classical theory. The scattering and reflection coefficients can be approximated by numerical and analytic methods. The main focus of this thesis lays on the analytic approximation. An iterative method is used that is derived from the general mixed potential integral equations for thin wires. The iteration is initialized by the classical transmission line solution. Each following solution depends on the previous iteration step. The analytic approximation is compared to a numerical one (method of moments) and a very good agreement is observed. Furthermore, the examples show the significantly improved accuracy compared to the classical transmission line theory. Moreover, the analytic and numerical approximations are compared to measurement results. The complex radar cross section of thin wires above a ground plane is measured and the complex resonant frequencies, the so called natural frequencies, are extracted. The analytic natural frequencies are obtained by using the asymptotic approach and the iterative method. Very good agreement between measurement, analytic and numerical solution is observed for multiple examples.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-45-3
-

Fritsch, Martin: Measurement of partial discharges on power cables : a step towards successful online monitoring
Vol. 98 (2024)The electrical distribution grids, which are mainly build on power cables, will face higher loads in the future and will thus play an increasingly important role in the power supply system. This is a problem because most power cables are already several decades old and the dielectric strength of their insulation deteriorates over time. Since the condition of the power cable insulation is usually unknown to the distribution system operators (DSO), the risk of cable failures will increase accordingly. To prevent costly supply interruptions, the DSOs require a condition-based maintenance strategy for their power cables. The most common method for condition monitoring is partial discharge (PD) measurement, which detects small electrical discharges occurring at insulation defects at an early stage. However, today’s PD sensors are usually not designed for continuous online monitoring and are often very expensive, which limits their usefulness for DSOs. This dissertation thesis aims to develop a cost-effective and reliable PD sensor for online monitoring of power cables. The research focuses on improving high-frequency current transformers (HFCT) to overcome magnetic saturation issues and optimize their sensitivity. The research begins by investigating the nature of PD signals transmitted along power cables and their measurable bandwidth. An analytical power cable model is developed to simulate the transmission process and determine the remaining bandwidth at the cable ends where the PD sensors are installed. Based on these findings, an optimized HFCT sensor design is investigated, which guarantees maximum sensitivity to PD pulses. For this purpose, an analytical HFCT model is derived. However, the challenge with HFCTs is their susceptibility to magnetic saturation caused by the high 50 Hz operating currents of power cables. To address this issue, an improved split-core HFCT design is proposed, capable of self-adjusting its air gap length based on the saturation level. A microcontroller controls a servo motor to optimize the air gap length in real-time, ensuring maximum sensitivity without saturation. This solution enables online monitoring of power cables using HFCT technology. The key contributions of this thesis include the improved split-core HFCT design with self-adjusting air gap length, an analytical power cable model for HF signal transmission, an analytical HFCT model for design optimization, and a method for real-time PD signal evaluation. Future work should focus on further optimizing the sensor design and integrating advanced methods for PD detection and signal evaluation.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-43-9
-
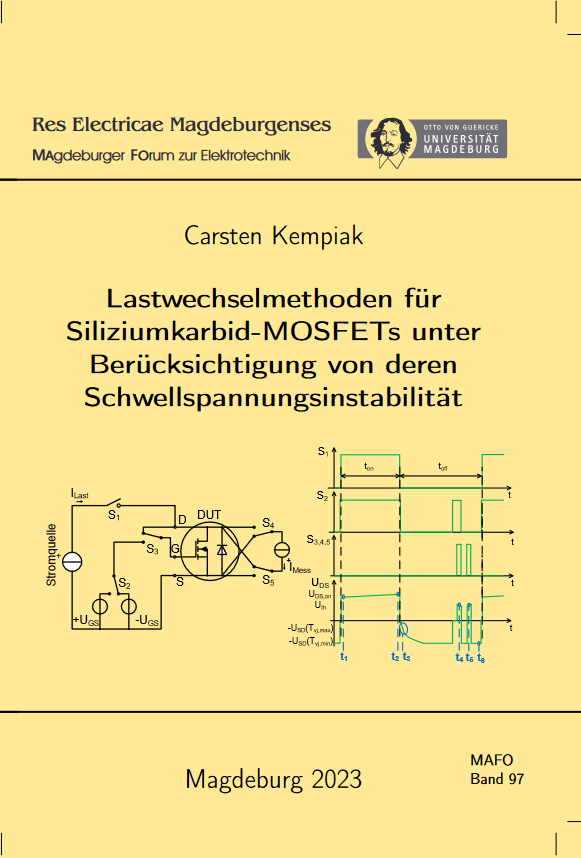
Kempiak, Carsten: Lastwechselmethoden für Siliziumkarbid-MOSFETs unter Berücksichtigung von deren Schwellspannungsinstabilität
Vol. 97 (2023)The application of established qualification test routines like power cycling to SiC MOSFETs is not as straightforward as it may seem: The threshold voltage Vth of SiC MOSFETs is not a stable parameter, affecting junction temperature sensing during the test execution and yielding an undesired shift of the turn-on resistance. Within this work, a Vth-monitoring concept is proposed and applied. Based on this approach, an extensive characterisation of Vth-instabillities under power cyclinge like gate conditions is carried out, the main influencing factors are identified and a concept to suppress parasitic drift effects during a power cycling test based on preconditioning is derived. The comparison of first power cycling results with and without prior applied preconditioning validates this approach and further implicates a significant impact of Vth on the test outcome. In addition, a junction temperarure measurement approach independent on Vth-instabilities based on a chip-integrated sensor is introduced and compared to the established VSD(T)-method. As result of this work, the main challenges of the application of power cycling tests to SiC MOSFETs are pointed out, methods dealing with them are proposed and verified by using special engineering samples as well as commercial SiC MOSFETs of different manufactures and voltage classes as exemplary devices under test.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-38-5
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/ub.ovgu-2023-102 -

Lindemann, Andreas; Wolter, Martin; Rose, Georg; Vick, Ralf (Hrsg.): 23. Dresdener Kreis Elektroenergieversorgung: Begleitband zum Workshop 2022 in Magdeburg
Vol. 96 (2023)Im Jahr 2022 war die Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg Ausrichter des alljährlichen
Treffens des „Dresdener Kreis“. Vom 15. bis zum 16. März nahmen neben dem
LENA (Lehrstuhl für Elektrische Netze und Erneuerbare Energie) auch Mitarbeitende der
Universitäten Dresden, Hannover und Duisburg-Essen am Doktorandenseminar teil.ISBN: 978-3-948749-33-0
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2023-094
-

Könneke, Nicola: Entwurf eines Testbetts für Assistenzsysteme in der Netz- und Systemführung
Vol. 95 (2023)On June 30, 2011, the Bundestag decided to completely phase out nuclear energy [1]. Furthermore, a complete exit from coal power was confirmed on June 3rd, 2020 [2]. These decisions led to a significant decline in conventional generators and thus to a significant reduction in the inertial flywheel masses in the grid. In addition, the share of renewable energy sources in gross electricity generation has increased in recent years from 18.9 TWh (1990) to 233.6 TWh (2021) [3]. At the same time, the highly dynamic power electronics in the network increased significantly. As a result of this transformation, the dynamics in the individual supply networks are noticeably increasing. In the future, it can no longer be accomplished with established network management concepts that have to be carried out completely manually. Accordingly, some network management processes must be partially or fully automated. Such an automation of the network management is considered in the present work. For this purpose, the basis of the developed test bed, the standard-compliant interface, is presented first. This includes an evaluation of the conditions contained in IEC-60870-5 regarding the communication structure and process as well as the composition of the respective telegrams. In addition, both technical and legal requirements of assistance systems are examined. The composition of the test bed is described in detail. The different functions of the communication partners (control room, interface and simulation environment) are illustrated. The connection setup, data exchange and setup of the assistance system used later are also part of this work step. The mathematical derivation of the calculations implemented in the simulation environment (load flow and sensitivity analysis) and the differences in content between redispatch and redispatch 2.0 conclude the analytical part of this work. The assistance system is then first outlined mathematically in order to be illustrated later using two different case studies. These case studies include a grid with 6 nodes from the 110 kV level and a complex network, which contains a replica of the transmission network of Saxony-Anhalt including neighboring stations and subordinate stations. Using these networks, both the functionality and the advantages of the assistance system are presented and documented. The associated simulations are based on measured values based on every quarter of an hour and cover a full year. In addition, several combinations are considered with regard to the feed-in behavior in the 6-node network.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-32-3
-

Woldu, Tahaguas: Modeling and simulation of power system dynamics for studying the impacts of increasing wind power in a weak grid system
Vol. 94 (2023)The issue of environmental concerns and efforts to decrease dependency on fossil fuel are bringing renewable energy resources to the mainstream of electric power generation. Wind energy has undergone fast expansions worldwide in recent decades, but it also results in challenges in system operation related to frequency and voltage stabilities. Investigating and evaluating the impact of large-scale wind power on power system dynamics is an essential step to enhance the stable operation of frequency and voltage. This thesis work is intended to investigate the impacts of wind power and propose mitigation measures to enhance the dynamic behaviors of power systems with various network topologies. Doubly-fed induction generator (DFIG) is the most common wind turbine type due to its ability to operate at variable wind speed, partial-load converter and its capability to sustain the generator in synchronism with the system during abnormal conditions. Therefore, in this thesis work, a detailed model of DFIG-based wind turbine generators is employed to illustrate the influence of increasing wind power share in a large network system. The network dynamic models include synchronous generators, automatic voltage regulators, turbine-governor systems, DFIG-based wind turbine generators, various control elements, transmission systems and transformers. The mathematical dynamic models are solved using numerical integration techniques. For this purpose, a power system dynamic simulation tool is developed in the MATLAB/Simulink environment. In this thesis work, four test networks, including a case study for the Ethiopian power system, are employed to simulate the dynamic responses in different network topologies. The various simulation scenarios and network topologies confirm that an increase in wind power share deteriorates the transient stability of a system. The results effectively show that the increase in wind power penetration level has contributed to reducing the dynamic voltage stability margins, increasing the rate of change of frequency and reducing active power transfer capability. Moreover, the DFIGs are observed to disconnect themselves from the grid in response to grid voltage dips under severe fault events so as to protect the back-to-back rotor-side converters from rotor over-currents. The dynamic impacts of DFIG-based wind generators are assessed and control strategies are proposed to help them not only to remain connected but also to support the system stability during grid fault events. A new control strategy is contributed to enhance the low voltage ride-through capability of DFIG-based wind generators. The proposed control strategy comprises a joint application of a STATCOM and rotor over-speeding schemes. The STATCOM is mainly employed to improve the stator voltage dip and the rotor overspeeding strategy is employed to reduce the rotor over-currents during stator voltage dips that results in reduced output power. The over-speeding scheme is initiated to adjust the active power reference to be proportional to the voltage dip at the terminal. Thus, the turbine is made to increase the rotor speed till the maximum allowable limit so that the output power remains reduced until the stator voltage dip is recovered by the fast-acting STATCOM. The second contribution is related to solutions to the grid frequency challenges with higher penetration level of wind power. A new approach is introduced by which wind power plant operators can schedule their wind power generations so as to give support in the frequency restoration process. The proposed frequency control module at plant level monitors the contribution of various operating units in a large wind farm, based on their respective wind speed and the grid frequency deviation. The time-domain simulation results indicate that the proposed voltage and frequency control strategies are efficient to regulate the real-time voltage dip and enhance the voltage and frequency controllability with higher penetration level of wind power.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-31-6
-

André Richter: Virtuelle Kraftwerke im Verteilnetz : systemstützender Betrieb im wirtschaftlichen Kontext : eine gesamtheitliche Betrachtung Virtueller Kraftwerke
Vol. 93 (2023)Mit der Zunahme von dezentralen, volatilen erneuerbaren Energien steigt auch die Schwierigkeit zur Stabilisierung des Energiesystems Strom. Insbesondere durch den Wegfall von konventionellen Kraftwerken ist es notwendig, geeignete Steuerungskonzep-te zu őnden und Systemdienstleistungen auch aus erneuerbaren Energien bereitzustellen, um ein zuverlässiges und stabiles System zu gewährleisten. Die vorliegende Dissertation liefert mit dem Konzept des Virtuellen Kraftwerks einen Ansatz zur Bündelung von kleinen, dezentralen, erneuerbaren Energien-Anlagen der Mittel- und Niederspannung. Mit dem hier vorgestellten Virtuellen Kraftwerk wird der große Nutzen von gepoolten Anlagen in den Prozessen der Netzbetreiber aufgezeigt und das Gesamtverständnis des techno-ökonomischen Stromsystems erweitert. Darüber hinaus liefert diese Dissertation die Least-Squares-Kombiprognose zur Verbesserung der PV- und Wind-Einspeiseprognose. Den Kernbeitrag stellt die Entwicklung und algorithmische Umsetzung von netzdienlichen Betriebsführungskonzepten für das Virtuelle Kraftwerk dar. Diese zielen auf die Maximierung der Bereitstellung von Regelleistung, Redispatchvermögen und auf die Einhaltung des Day-Ahead-Fahrplans ab. Zudem werden wirtschaftliche Betriebskonzepte umgesetzt, die als ökonomischer Maßstab zur Bewertung der netzdienlichen Konzepte herangezogen werden. Anhand eines exemplarischen Virtuellen Kraftwerks werden die Algorithmen getestet und der große Nutzen der Betriebskonzepte sowie eine Wirtschaftlichkeit (auch ohne EEG-Förderung) nachgewiesen. Abschließend liefern die Analysen Anhand eines Mittelspannungstestnetzes eine Einordnung des Virtuellen Kraftwerkbetriebs in die Netzbetriebsführung. Zu diesem Zweck wird das Cigré-Benchmarknetz rein mit erneuerbaren Energien und Lasten auf Basis von statistischen Werten von EE-dominierten Verteilnetzbetreibern parametrisiert.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-28-6
-

Muhammad Tayyab: Holistic approach for microgrid planning and operation for e-mobility infrastructure under consideration of multi-type uncertainties
Vol. 92 (2022)Integrating renewable energys ources in sectors such as electricity, heat, and transportation must be structured in an economic, technological, and emission- efficient manner to address global environmental issues.Microgrids appear to be the solution for large-scale renewable energy integration in these sectors.The microgrid components must be optimally planned and operated to prevent high costs, technical issues, and emissions. Existing approaches for optimal microgrid planning and operation in the literature do not include a solution for e-mobility infrastructure. As a consequence, a compact e-mobility infrastructure metho- dology is provided.The development of e-mobility infrastructure has as sociated uncertainties (short and long-term). As a result, a new stochastic method re- ferred to as IGDM-DRO is proposed in this dissertation.The proposed method provides a risk-averse strategy for microgrid planning and operation by including long-term and short-term uncertainty related to e-mobility.The multi-cut ben- der decomposition is applied for IGDM-DRO to prevent the suggested method’s intractability.Finally, the deterministic and stochastic methodologies are com bined in an ovelholistic approach for microgrid design and operation in terms of cost and robustness.The proposed method ist ested on a new settlement area in Magdeburg, Germany, under three different EV development scenarios (nega- tive, trend, andpositive).The share for the number of electric vehicles reached 31 percent of conventional vehicles by the end of the planned horizon. As a result, the microgrid’s overall cost has been increased by 2.3 to 2.9 percent per electric vehicle.Three public electric vehicle charging stations will be required in the investigated settlement are a intrend 2031.The investigated settlement area will require a total cost of 127,029 € in the trend scenario.To achieve full robustness against long-term uncertainties,the cost of the microgrid needs to be increased by 80 percent.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-25-5
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2022-084
-

Dancker, Jonte: Sensitivity Factors for Integrated Energy Systems: A Joined Quasi-Steady-State Approach
Vol. 91 (2022)Integrated energy systems can increase the use of volatile renewable energy generation while reducing operation cost in the electric power system. The benefits result from shifting energy between energy infrastructures and using the network storage capability of district heating and gas systems. But the more strongly the different energy systems are linked the more complex their operation becomes. To ensure a secure and reliable system operation while using the full potential of integrated energy systems the interactions and the network storage effects of the district heating and gas system must be analyzed. Existing power flow calculation methods of integrated energy systems, however, neglect the network storage effects which result from the dynamic behavior of the district heating and gas system. The dynamic behavior is only investigated if the different energy systems are solved separately. As existing methods do not directly represent the interactions and effects of the dynamic behavior in an integrated energy system, the effect of any unit's power change on the power flows in the integrated energy system can only be determined by a complete power flow calculation, leading to a high computational cost. To reduce the computational cost this thesis derives sensitivity factors estimating the effect of a power change on the system state of an integrated energy system. To derive the sensitivity factors a joined quasi-steady-state power flow calculation method for integrated energy systems is developed extending existing steady-state approaches. For this, the system state of the electric power system, district heating system, and gas system is determined simultaneously, directly representing their interactions. To include the dynamic behavior a gradient method is proposed, which allows temperature and calorific value changes to be tracked in a coupled power flow calculation. The gradient method can accurately depict the dynamic behavior in the joined quasi-steady-state power flow calculation method even with simulation time increments of up to 60 min. Hence, compared to existing methods larger simulation time increments can be chosen to reach the same accuracy, leading to a reduced computation time. The sensitivity factors are on average ten times faster in estimating a new system state after a unit's power change compared to a power flow calculation. Besides the high computational efficiency, they can provide good estimates considering the complexity of the interactions and the dynamic behavior in an integrated energy system. As the joined quasi-steady-state power flow calculation method is based on the steady-state analysis existing use cases can be easily extended to consider the full potential of integrated energy systems. Therefore, the thesis provides system operators with a method to accurately analyze the full potential of Integrated energy systems.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2022-81
ISBN: 978-3-948749-24-8
-

Willmann, Benjamin: Elektromagnetische Umweltverträglichkeit eines Elektrofahrzeugs mit kontaktlosem Ladesystem
Vol. 90 (2022)When developing electric vehicles with wireless power transfer systems (WPT system), the human exposuire with respect to electromagnetic fields (EMF) must be secured. With the help of two newly developed methods, the EMF behavior of electric vehicles with a WPT system can be estimated at an early stage of development by using existing EMC component tests according to CISPR 25. It is possible to consider both reference levels and base restrictions. So that the internal electric field strength can be calculated for a human body model, an extension of an existing field solver by volume integral equations is presented. Later on this method is verified for the human model TARO. The first method models WPT systems from construction data and parameterizes them through a combination of network analysis and the theory of reflected loades. Verification can be carried out through magnetic field measurements during component testing. An EMF assessment of the WPT system can then be carried out in a simulation with the model of a car body. Magnetic fields also occur in the interior of a vehicle. These are mostly caused by the electrical currents of the energy supply systems. The second method presented, the current-based EMF assessment, offers the possibility to achieve a prototype-free development with respect to EMF guidelines. For this purpose, current limit values for each component of interest are first derived from the reference value functions of applicable EMF guidelines in combination with line and car body data of a virtual prototype. These can then be used in a CISPR 25 component test for the EMF assessment of the measured currents.
DOI: https://doi.org/102435 2/UB.OVGU-2022-054
ISBN: 978-3-948749-19-4
-

Pribahsnik, Florian Peter: Gallium Nitride (GaN) specific mechanical phenomena and their influence on reliability in power HEMT operation
Vol. 89 (2022)In recent years Gallium Nitride (GaN) has entered the market for power devices on a broader scale, increasing the need for a deeper understanding of fundamental interactions within such devices. Extensive research has been conducted in the field of electric effects since the main differences of GaN over Silicon (Si) lie there. In contrast to this, this thesis will focus on new mechanical and thermo-mechanical phenomena, previously not occurring in Si devices. Chapter 3 will introduce the interactions of the mechanical stress, the temperature and the electric field. The effects connecting these state variables are explained in detail and it will be shown which effects can be neglected and which ones need closer investigations. In Chapter 4 the thermal capabilities under massive thermal overload, caused by a short circuit pulse, are discussed. The setup, which is used to stress the chips until failure, is presented. Failed devices are analyzed extensively by in depth physical failure inspection methods. Root cause analysis is done by means of Finite Element Analysis (FEA) and in depth physical failure analysis, finally enabling to provide suggestions for improvements in this particular failure mode. Chapter 5 will elaborate on resonance phenomena in GaN. Since GaN is piezoelectric it can act as an actuator to resonate the whole chip assembly. This phenomenon is measured in two steps and subsequently investigated by FEA. The Finite Element (FE) simulation results are validated against the measurements to ensure the correctness of the FE model. From these simulations conclusions regarding the reliability of the two most failure prone layers, namely the GaN stack and the die attach layer, are drawn. Additionally extreme cases are discussed giving an outlook on this issue in advanced package assemblies.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2022-051
ISBN: 978-3948749-17-0
-
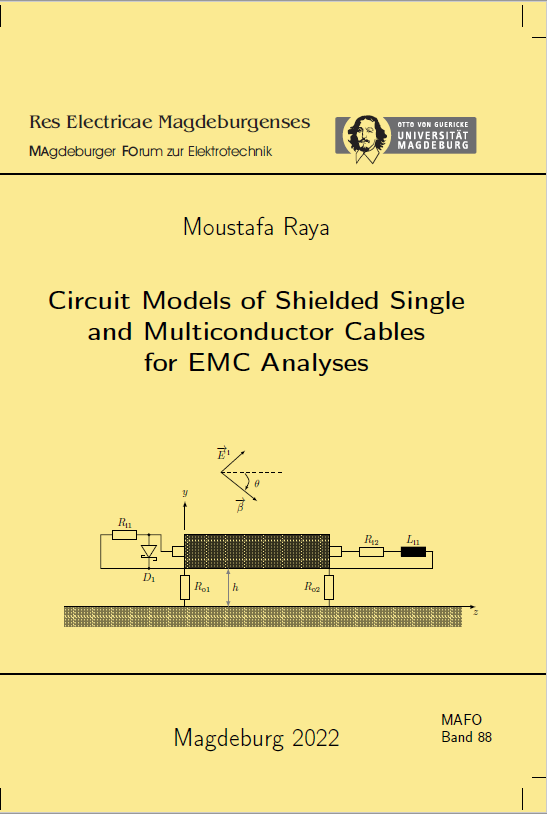
Raya, Moustafa: Circuit models of shielded single and multiconductor cables for EMC analyses
Vol. 88 (2022)In this thesis, novel circuit models for coaxial cables with braided shields placed above a ground plane are presented. The models are derived from the transmission line theory and are suitable for integration into SPICE simulation programs. Two types of models are presented. First, a lumped-circuit model is developed in which the cable is divided into small sections, with each section replaced with an equivalent circuit and connected to represent the entire cable. In the second type, a macromodel is developed from the analytical solutions of the transmission line theory to represent the entire cable without discretizing it. This work demonstrates the efficiency of the macromodel in terms of computing time and accuracy compared to the lumped-circuit model. The designed models can be used to calculate the induced voltage at the termination loads of the cable when an incident uniform plane wave is coupled in. These models can also calculate the coupling results due to interference from lumped sources. The developed models are therefore suitable for the circuit EMC analysis of systems that contain shielded cables and are susceptible to field coupling or interference with other systems. The bidirectional coupling between the inside and outside of the cable shield is taken into account, which enables the analysis of interference immunity and emissions. The mathematical functions for calculating the coupling between the inner and outer systems of the cable are transformed into equivalent circuit diagrams that allow the models to be used in the frequency domain or together with nonlinear elements in the time domain. The developed models for a single conductor shielded cable are expanded for shielded multiconductor cables within the scope of this work. The circuit models are validated by measurements and field simulations, and the results show excellent agreement.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2022-037
ISBN: 978-3-948749-16-3
-

Abschlussbericht zum Verbundprojekt InKoLa : Infrastrukturkopplung - Platzierung und Betrieb von Ladestationen aus Verkehrs- und Energienetzsicht
Vol. 87 (2022)Im Mittelpunkt des Vorhabens InKola „Infrastrukturkopplung – Platzierung und Betrieb von Ladestationen aus Verkehrs- und Energienetzsicht“ steht die infrastrukturübergreifende Planung und der Betrieb für Verkehr- und Energiesysteme.
Das Ziel ist es, zusammen der Stadt Burg ein anwendungsorientiertes Konzept zur optimalen Platzierung, Versorgung und Betrieb von Ladeinfrastruktur aus Netz- und Verkehrssicht unter Einbindung erneuerbarer Erzeugung zu entwickeln, und an ausgewählten Standorten in der Stadt Burg Ladeinfrastruktur zu installieren.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2022-014
ISBN: 978-3-948749-15-6
-
Analysis of the stochastic electromagnetic field coupling to single and multiconductor transmission line structures
Vol. 86 (2021)This thesis analyzes transmission lines and their behavior in a reverberation chamber. For this purpose, a time efficient closed-form solution for the coupling of stochastic electromagnetic fields to single- and multiconductor transmission line structures is presented. The simulation model is based on the Baum-Liu-Tesche (BLT) equations, but this thesis goes beyond the study of a coupling to a single plane wave and studies the excitation by a stochastic field. The transmission lines are described analytically using transmission line theory and in addition per-unit-length (p. u. l.) parameters are defined. Based on Maxwell’s equations, a generalized transmission line theory is presented which, however, resembles classical transmission line theory in its structure. The classical transmission line theory is extended to include higher order modes. A high frequency (HF) model is derived for the p. u. l. parameters, in that way that the parameters become frequency dependent. The model of the frequency dependent p. u. l. parameters is deduced and validated by the method of moments and by measurements in the reverberation chamber. Different configurations of the transmission line structures are analyzed and the average magnitude of the coupled voltage at the terminals is calculated and discussed. Moreover, the influence of bending transmission lines and its influence on the field-to-wire coupling is investigated.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2021-105
ISBN: 978-3-948749-13-2
-

Pannicke, Enrico: Empfangsspulen für bildgeführte Eingriffe mittels Magnetresonanztomographie
Vol. 85 (2021)Magnetic resonance imaging offers superior soft tissue contrast, the ability to align slices at will, and non-invasive thermometry. For performing minimally invasive image-guided interventions, these features provide an invaluable advantage over other imaging modalities, such as computed tomography (CT). This is because the superior soft tissue contrast makes it possible to visualize even small target structures, thus enabling reliable puncture. The selection of oblique slices also makes it possible to safely bypass any risk structures. Nevertheless, the performance of such procedures under MR imaging has never been able to gain widespread acceptance over the past 20 years. A major reason for this is the complex workflow of such procedures, which are only performed at a few centers due to the lack of standardized instruments and procedures. The solutions established there are characterized by a high degree of individuality and poor transferability. The so-called „MR-receive coils“ are of enormous importance for the safe performance of such interventions - after all, they essentially determined the image quality. Therefore, the aim of this dissertation is to investigate a concept for a dedicated interventional MR receive coil. The purpose of this concept is to significantly simplify the placement and preparation of an MR receive coil required for the intervention. To this end, new approaches to so-called „power matching“ and „active decoupling“ are presented. These allow to redefine the usual topologies of MR receive coils and to gain further degrees of freedom in the implementation. This approach differs fundamentally from comparable studies that consistently rely on component substitution to increase flexibility. The approaches presented are analyzed in detail and corresponding procedures for correct dimensioning are developed. The latter thus serve as a basis for an engineering approach and are validated experimentally. Both sub-approaches were integrated in the demonstrator of a dedicated interventional coil and evaluated by means of laboratory and MR measurements. It could be shown that the newly introduced approaches provide comparable results to the state of the art established methods. In summary, it can thus be stated that the contributions presented in this work enable the implementation of interventional „disposable“coils.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-12-5
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2021-096 -

Zhang, Yonggang: Analysis and control of resonances in HVDC connected DFIG-based offshore wind farm
Vol. 84 (2021)Interactions among the widely utilised converter-interfaced grid components and passive grid components can introduce wide-frequency range of resonances, thus induce massive harmonic distortions and even endanger system stability. Their consequences might be the tripping of renewable and conventional generation units or the physical damage of sensitive grid assets. Motivated by recent years’ resonance incidents in wind-integrated power systems, this study investigates the resonance-induced harmonic distortion and stability issues in doubly fed induction generator (DFIG)-based offshore wind farm (OWF) with high-voltage direct current (HVDC) grid connection. The objective of this study is to accurately characterize the resonances, evaluate their risks and provide solutions for the design of mitigation strategy. To accurately capture the dynamic characteristics of DFIG-based wind farm, a comprehensive impedance modelling considering the detailed PI control loop and DC dynamics of wind turbine as well as the cable connections of the medium-voltage (MV) collector system is conducted. Through stepwise simulation verifications, aggregated modelling of MV collector system is proved to be suitable for wideband resonance analysis. On this basis, both Bode-plot method and resonance mode analysis (RMA) approach have been adopted to address the resonance issues taking into account various wind farm operating conditions and grid topology changes. Their impacts on resonance frequency, harmonic amplification level and damping level are investigated. The locations where resonances can be most easily excited are identified through bus participation factor analysis. Moreover, the impact of the frequency-coupling effects from asymmetrial converter control and switching operations on subsynchronous resonance (SSR), middleand high-frequency resonances is analyzed using the aggregated models derived from a practical HVDC connected DFIG-based OWF. Large harmonic distortion and stability issues are demonstrated for the frequency range from several Hz to a few kHz. In order to prevent the negative impact of resonances on power quality and system stability, a series of active damping possibilites have been studied and implemented in the studied wind-integrated power system, and a coordinated damping strategy which can effectively damp wideband resonances is proposed. Finally, simulations in MATLAB/Simulink validate the results of impedance modelling, resonance analysis as well as the effectiveness of the wideband resonance damping strategy.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-05-7
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2021-062 -

Gerlach, Andreas: Regelung von direktangetriebenen elektrischen Maschinen für Verbrennungsmotoren
Vol. 83 (2021)This work deals with the control of electrical machines that are directly coupled to an internal combustion engine. At the beginning, some basics for the control of permanently excited synchronous machines and the functioning of four-stroke gasoline engines are explained. This is followed by the various test setups that were used in this work to validate various average and dynamics-based control
procedures. The average value-based control methods include methods that do not require a
highly dynamic change in torque within the four cycles of the internal combustion engine. This includes throttle actuator-free power control. The system is nonlinear. To control the system, it was linearized on the one hand by using a Taylor approximation and on the other hand by using a feedback linearization. A controller could then be designed for the linearized system. Another control method, based on average values, is the control without an angle encoder. Here, angle estimation methods for the PMSM were used to estimate the electrical angle and the torque of the internal combustion engine, which is compared with a theoretical compression torque in order to reference the crank angle to the electrical angle. The dynamics-based control methods are methods that change the torque / force
curve of the electrical machine significantly within the four cycles. This makes it possible, among other things, to adapt the piston stroke in an internal combustion engine with a crankshaft and in a free piston engine. In addition, the injection of a highly dynamic torque on a camshaft can be used to adjust the valve timing. High control dynamics are also necessary when an almost constant speed is required. For this, a torque must be applied, which compensates the torque of the internal combustion engine. This is known as torque damping / compensation. Different torque damping methods were tested and the results compared according to implementation effort and required sensors.ISBN: 978-3-948749-03-3
DOI: https://doi.org/1024352/UB.OVGU-2021-056 -

Liu, Yu: Contribution to improve the EMI performance of electrical drive systems in vehicles with special consideration of power semiconductor modules
Vol. 82 (2021)This work serves as a contribution to improve the EMI performance of electrical drive systems in vehicles; the focus is on the power semiconductor module for automotive application. For a better and deeper understanding of the conducted EMI source, the conducted EMI mechanisms and effects in the drive system are investigated through simulations as well as measurements with special consideration of power modules: The influence of the diode recovery effects on the EMI performance is quantitatively analyzed with different load currents, as well as with different types of diodes, e.g. SiC Schottky barrier diode. Through the simulation, the influence coming from the power module to the system is clarified; the importance of different factors inside and outside of the power module regarding EMI performance are therefore evaluated. To validate the simulation results, the setup and test bench for a conventional EMI measurement for the typical automotive application are presented. Through the measurement results it is proven that the simulation models are usable under certain boundary conditions for future power module designs with regard to the EMI prediction. Based on the understanding and the conclusions from the simulation and measurement results, concrete EMI optimization concepts for an inherently low-interference power module are developed and realized. The EMI performance as well as the feasibility of the sample modules are compared and evaluated under different criteria from the power module manufacturer’s point of view. Besides, the dynamic and short-circuit performances of the sample modules, regarding to the current distribution on the semiconductor chips, are characterized. A novel test procedure is introduced in this work, by which it is possible to estimate the conducted EMI performance of power modules without building the whole test setup like in a conventional EMI measurement. This characterization can subsequently be used in the phase of converter development to select a suitable device and evaluate the expected effort to comply with EMI standards.
ISBN: 978-3-948749-01-9
DOI: https://doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2021-055 -

Middelstädt, Lars: Transiente Effekte in leistungselektronischen Schaltungen mit schnellschaltenden Leistungshalbleitern unter besonderer Berücksichtigung der elektromagnetischen Verträglichkeit
Vol. 81 (2020)Das Schalten von neuen Leistungshalbleitern innerhalb von wenigen ns stellt hohe Ansprüche an ein korrespondierendes Schaltungslayout sowie an das Design passiver Komponenten im Bezug auf minimierte parasitäre Elemente. Dies ist unter anderem für die elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit von Bedeutung. Diese Arbeit analysiert und bewertet transiente Effekte von schnellschaltenden Leistungshalbleitern mit speziellem Fokus auf die elektromagnetische Verträglichkeit und schlägt Maßnahmen zur Verbesserung vor. Das erhöhte Störpotential von Schaltungen mitWide Bandgap-Transistoren gegenüber Schaltungen mit konventionellen Si-IGBTs wird im Detail untersucht. Anhand eines beispielhaften DC/DC-Wandlers werden allgemeingültige Designrichtlinien für passive Komponenten sowie für das Schaltungslayout entwickelt. Hierbei werden sowohl die intra-EMV als auch geleitete und gestrahlte Störungen anhand von Messergebnissen analysiert und bewertet. Untersuchungen zum Einfluss von Halbleiterparametern zeigen deutlich, dass schaltbedingte Oszillationen im Resonanzkreis der Kommutierungszelle entstehen und parasitäre Antennenstrukturen anregen. Dadurch wird das Störspektrum oberhalb von 30MHz maßgeblich vergrößert. Die zur selektiven Analyse des Schaltverhaltens im Frequenzbereich entwickelte Methode ermöglicht es, zwischen den Einflüssen des Ein- und Ausschaltverhaltens auf das Störspektrum zu unterscheiden. Anhand von experimentellen Parametervariationen werden so vereinfachte Modelle für die Ein- und Ausschaltoszillation extrahiert. Auf deren Basis können analytische Ausdrücke unter der Beachtung der Anfangswerte aufgestellt werden. Diese vermitteln ein grundlegendes Verständnis konkreter Ursachen der Anregung der Oszillationen. Darauf aufbauend wird in dieser Arbeit eine Optimierungsstrategie entwickelt, um Schaltoszillationen zu vermeiden. Hiermit werden die Oszillationen durch genau eingestelltes Schalten minimiert. Somit ist es möglich, mit einer mittleren Schaltgeschwindigkeit zeitgleich Schaltverluste zu reduzieren und EMV-kritische Oszillationen zu eliminieren. Für das Einschalten bedeutet dies das korrekte Einstellen der Überstromspitze. Dass dies über die Gate-Ansteuerung umsetzbar ist, wird anhand von Simulationen sowie Versuchen gezeigt. Als einfachster Ansatz stellt ein RC-Glied im Gate-Kreis das Schaltverhalten bei definierter Stromsteilheit variabel ein und führt so zu einer Eliminierung der Einschaltoszillation. Bestätigt wird dies an einem Doppelpulsversuchsstand mit CoolMOS MOSFET und SiC Schottky Diode. Eine Alternative sind aktive Treiber. Simulationsergebnisse zeigen, dass bereits ein zusätzlicher Transistor im Gate-Kreis zur Minimierung von Oszillationen im Lastkreis beitragen kann. Der Einsatz eines integrierten aktiven Treibers mit einstellbarem Gate-Profil in einem Brückenzweig mit GaN HEMTs bestätigt die Validität der entwickelten Strategie. Sowohl eine effiziente Vorgehensweise zur Erstellung eines optimierenden Gate-Profiles als auch validierende EMV-Messungen der gestrahlten Störungen werden vorgestellt. Somit zeigen sowohl Simulations- als auch Messergebnisse die Anwendbarkeit der Optimierungsstrategie und deren positiven Einfluss auf das EMV-Verhalten für unterschiedliche Schaltungen und Leistungshalbleiter.
ISBN: 978-3-944722-95-5
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.24352/UB.OVGU-2020-148
-

Petzold, Jörg: Analytische Beschreibung der Kopplung elektromagnetischer Felder durch Aperturen in Resonatoren
Vol. 80 (2020)In this thesis a new systematic formalism of the coupling of electromagnetic fields between different radiation environments is derived from the basics of electromagnetic field theory. Here, the case of the coupling between a half space and a rectangular cavity is treated, which is a model for typical housings of electrical devices. An analytical solution is derived under the condition of electrically small apertures and then validated with numerical methods. Then the developed method is generalized for an simple electrical large aperture. It is made use of the duality of the Maxwell equations by the modeling of the generated current in an electrical large, thin, straight and finite wire in free space. The respective integral equation for the electrical field is solved in a new way by a combination of the methods of regularization and discretization. One of the unique properties of the derived matrix equation is the possibility to calculate all matrix elements analytically and therefore quite fast. Subsequently, the method is applied to the electrical large, thin, straight and finite slot in a rectangular cavity. The complete matrix is separated in a near and far interaction part. This way, different radiation conditions can be considered easily. The analysis of the far field of such a slot shows, the influence of the inner cavity resonances on the external fields can be calculated efficiently.
ISBN: 978-3-944722-91-7

